| Ground | LNS_GND | Lancaster Ground | 121.800 | HN |
| Tower | LNS_TWR | Lancaster Tower | 120.900 | HM |
| ATIS | KLNS_ATIS | 125.670 |
Rev. 2 — Revised: 2025-03-01
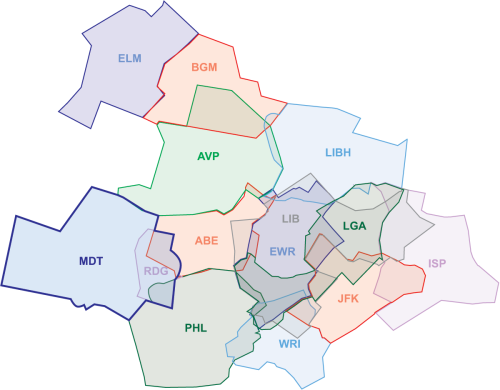
Area at a glance
| ICAO Code | Airport Name | Airspace |
|---|---|---|
| KLNS | Lancaster Airport | D |
- Purpose
- This document prescribes the procedures to be utilized for providing air traffic control services at Lancaster Air Traffic Control Tower (ATCT). The procedures described herein are supplemental to the New York ARTCC Standard Operating Procedures and FAA Order JO 7110.65.
- Distribution
- This order is distributed to all New York ARTCC personnel.
- Procedural Deviations
- Exceptional or unusual requirements may dictate procedural deviations or supplementary procedures to this order. A situation may arise that is not adequately covered herein; in such an event use good judgment to adequately resolve the problem.
Operational Positions
| Sector | Callsign | Frequency | Identifier | Combined Sector |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Harrisburg (HAR) | MDT_SW_APP | 124.100 | HK | Primary TRACON |
| Lancaster (LRP) | MDT_SE_APP | 126.450 | HS | |
| Ravine (RAV) | MDT_N_APP | 118.250 | HG | |
| Reading | RDG_APP | 125.150 | RX | Covered by MDT TRACON 0000-0600 local time |
Notes:
- When RDG_APP is not staffed, MDT TRACON may provide top-down services at RDG regardless of local time.
- When splitting MDT TRACON, split into HAR & LRP sectors first.
ATCT
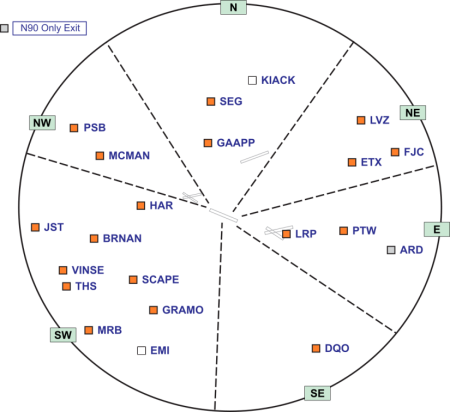
Clearance Delivery
| Exit Gate | Exit | Scratchpad |
|---|---|---|
| North (N) | GAAPP | GAA |
| SEG | SEG | |
| Northeast (NE) | ETX | ETX |
| LVZ | LVZ | |
| FJC | FJC | |
| East (E) | LRP | LRP |
| PTW | PTW | |
| ARD | ARD | |
| Southeast (SE) | DQO | DQO |
| Southwest (SW) | HAR | HAR |
| BRNAN | BRN | |
| JST | JST | |
| VINSE | VIN | |
| THS | THS | |
| SCAPE | SCA | |
| GRAMO | GRA | |
| MRB | MRB | |
| EMI | EMI | |
| Northwest (NW) | MCMAN | MCM |
| PSB | PSB |
Notes
- While strict exit direction points are not required at LNS, the guide above may come in handy for directing pilots to proper exits for departing the area.
- KIACK is only a valid exit of preceded by GAAPP. The route must therefore read GAAPP KIACK...
- MCMAN is used for aircraft routed via V33/J64/Q62.
- Traffic filed via EMI to join J48 should be re-routed via GRAMO VINNY EMI.
| Position | Frequency | Code |
|---|---|---|
| MDT_SE_APP | 126.45 | HS |
| MDT_E_APP | 126.450 | HS |
| MDT_APP | 124.100 | HK |
| NY_CTR | 125.325 | N56 |
The table above lists the common frequencies used as departure frequency by LNS Clearance Delivery. The first available controller in this list should be handling departures.
Note that this table only serves as a guide. The actual departure frequency has to be determined based on coordination with the other online controllers.
If there is no other controller online that would accept departures from LNS, use LNS CTAF (120.900).Routing to certain airports in ZNY, ZDC and ZBW ARTCCs is pre-coordinated through letters of agreement (LOA). These routes have been added to the Preferred Route Database (PRD). Therefore, PRD must be referenced for all departures.
Notes
- The initial altitude for IFR departures of all types is 3,000’ whereas higher may be expected in 10 minutes after departure.
- There is no published departure procedure out of Lancaster. All aircraft must be cleared to their destination via radar vectors to an LNS exit.
- Traffic filed via EMI to join J48 should be re-routed via GRAMO VINNY EMI.
Lancaster is a Class D airport. All VFR traffic must maintain two-way radio communication. See the VFR Operations document for detailed explanation of applicable VFR procedures.
Ground Control
- Departure Sequencing
| Exit Gate | Exits |
|---|---|
| North | GAAPP, SEG |
| Northeast | ETX, LVZ, FJC |
| East | LRP, PTW, ARD |
| Southeast | DQO |
| Southwest | HAR, BRNAN, JST, VINSE, THS, SCAPE, GRAMO, MRB, EMI |
| Northwest | MCMAN, PSB |
Aircraft should be sequenced to depart in the following order:
- By alternating gate group.
- If not the above, then by alternating exit.
- If not the above, then by aircraft type largest to smallest.
- Runway Ownership and Crossings
- Closed runways shall be owned by Ground Control. The only time runways will ever be closed is during events, and closures must be authorized by the TMU. We do not simulate runway closures on VATSIM during standard day-to-day operations.
- Transfer of runway ownership, between Ground Control and Local Control, shall be accomplished verbally (or textually).
- Ground Control is authorized to cross all active runways with coordination with Local Control.
- Aircraft Movement
- As the taxiway system is simple, there are no pre-defined routings.
- Since there are no parallel taxiways, you may use each taxiway as a two-way road whereby aircraft may be taxied in the opposite direction on the same taxiway at the same time. When you do this, ensure that both aircraft are told to watch out for the other. This procedure is only available to single engine props during daylight hours as they are narrow enough to be able to fit two abreast.
- When the above is not possible, hold departures on the ramp until the inbound aircraft is clear of the outbound aircraft. You may use conditional taxi instructions to accomplish this.